Solo para fines didácticos, y como complemento para los ejercicios presentados en la unidad para Ecuaciones Diferenciales Parciales, se presentan las instrucciones para las animaciones usadas en la presentación de los conceptos y ejercicios. Los algoritmos para animación NO son necesarios para realizar los ejercicios, que requieren una parte analítica con al menos tres iteraciones en papel y lápiz. Se lo adjunta como una herramienta didáctica de asistencia para las clases.
EDP Parabólica [ concepto ] [ ejercicio ]
1. EDP Parabólicas método explícito
Método explícito EDP Parabólica lambda: 0.25 x: [0. 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1. ] t: [0. 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1 ] ... 1.0 Tabla de resultados en malla EDP Parabólica j, U[:,: 10 ], primeras iteraciones 10 [60. 48.23 38.42 31.65 27.85 26.33 26.43 27.89 30.76 34.96 40. ] 9 [60. 47.67 37.58 30.86 27.29 25.96 26.11 27.53 30.39 34.71 40. ] 8 [60. 47.02 36.63 30.03 26.75 25.64 25.82 27.16 29.99 34.44 40. ] 7 [60. 46.25 35.56 29.15 26.25 25.37 25.56 26.78 29.53 34.11 40. ] 6 [60. 45.34 34.34 28.23 25.79 25.17 25.35 26.38 29. 33.72 40. ] 5 [60. 44.21 32.93 27.29 25.41 25.05 25.18 25.98 28.4 33.23 40. ] 4 [60. 42.77 31.29 26.37 25.14 25. 25.06 25.59 27.7 32.62 40. ] 3 [60. 40.86 29.38 25.55 25. 25. 25. 25.23 26.88 31.8 40. ] 2 [60. 38.12 27.19 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25.94 30.62 40. ] 1 [60. 33.75 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 28.75 40. ] 0 [60. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 25. 40.] >>>
Instrucciones en Python
# EDP parabólicas d2u/dx2 = K du/dt # método explícito,usando diferencias divididas # Referencia: Chapra 30.2 p.888 pdf.912, Rodriguez 10.2 p.406 import numpy as np # INGRESO # Valores de frontera Ta = 60 Tb = 40 #T0 = 25 # estado inicial de barra fx = lambda x: 25 + 0*x # función inicial para T0 a = 0 # longitud en x b = 1 K = 4 # Constante K dx = 0.1 # Tamaño de paso dt = dx/10 n = 100 # iteraciones en tiempo verdigitos = 2 # decimales a mostrar en tabla de resultados # PROCEDIMIENTO # iteraciones en longitud xi = np.arange(a,b+dx,dx) fi = fx(xi) m = len(xi) ultimox = m-1 ultimot = n-1 # Resultados en tabla u[x,t] u = np.zeros(shape=(m,n+1), dtype=float) # valores iniciales de u[:,j] j = 0 u[0,:]= Ta u[1:ultimox,j] = fi[1:ultimox] u[ultimox,:] = Tb # factores P,Q,R lamb = dt/(K*dx**2) P = lamb Q = 1 - 2*lamb R = lamb # Calcula U para cada tiempo + dt tj = np.arange(0,(n+1)*dt,dt) j = 0 while not(j>ultimot): # igual con lazo for for i in range(1,ultimox,1): u[i,j+1] = P*u[i-1,j] + Q*u[i,j] + R*u[i+1,j] j=j+1 # SALIDA np.set_printoptions(precision=verdigitos) print('Método explícito EDP Parabólica') print('lambda: ',np.around(lamb,verdigitos)) print('x:',xi) print('t:',tj[0:len(xi)],'...',tj[-1]) print('Tabla de resultados en malla EDP Parabólica') print('j, U[:,:',ultimox,'], primeras iteraciones') for j in range(ultimox,-1,-1): print(j,u[:,j]) # GRAFICA ------------ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt tramos = 10 salto = int(n/tramos) # evita muchas líneas if (salto == 0): salto = 1 for j in range(0,n,salto): vector = u[:,j] plt.plot(xi,vector) plt.plot(xi,vector, '.',color='red') plt.xlabel('x[i]') plt.ylabel('u[j]') plt.title('Solución EDP parabólica') #plt.show()
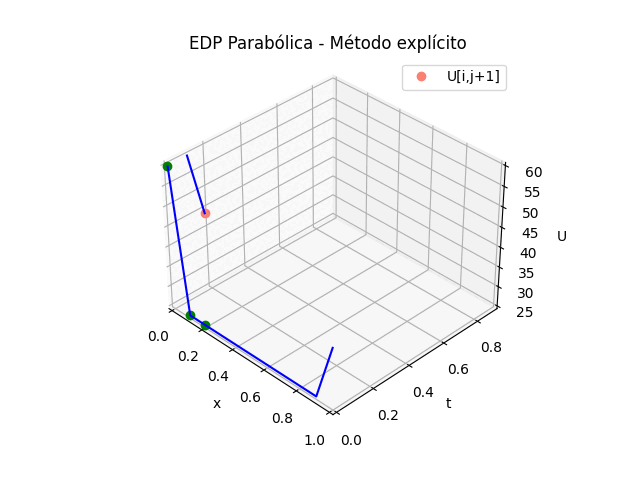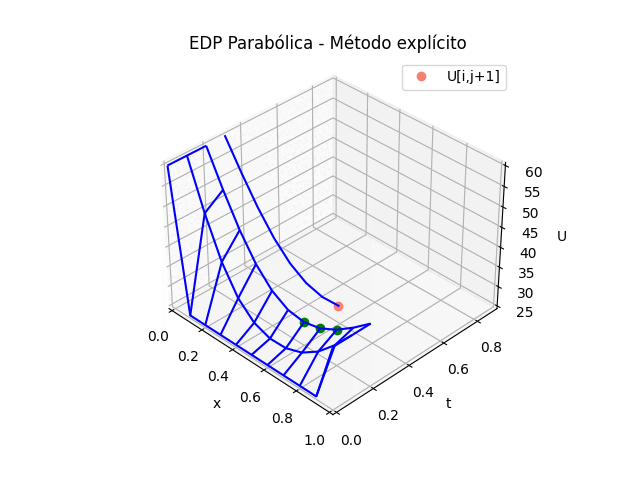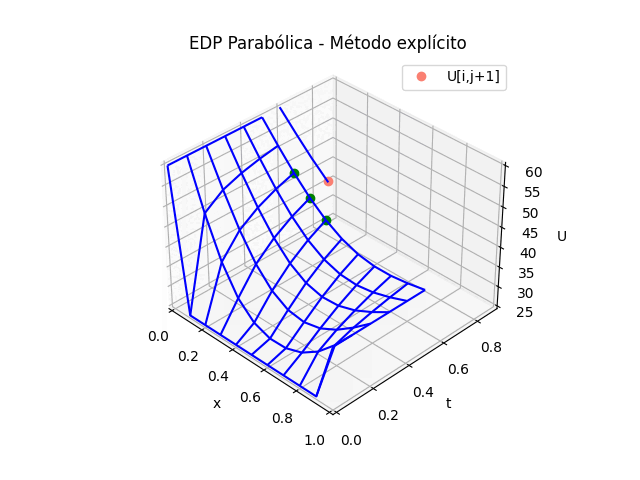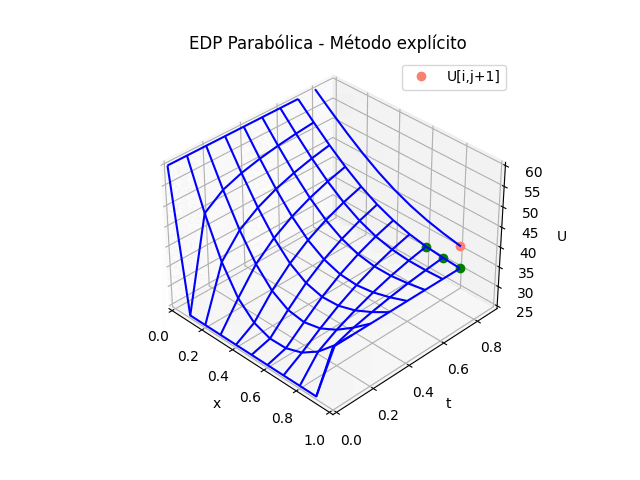
1.2 Gráficas EDP Parabólica, método explícito en 3D
Esta sección es la base para la generación de las animaciones siguientes, por lo que debe ser incluida antes de las dos siguientes animaciones 2D o 3D. Al menos hasta la parte donde se realiza la transpuesta de U.
# GRAFICA en 3D ------ tj = np.arange(0,n*dt,dt) tk = np.zeros(tramos,dtype=float) # Extrae parte de la matriz U,acorde a los tramos U = np.zeros(shape=(m,tramos),dtype=float) for k in range(0,tramos,1): U[:,k] = u[:,k*salto] tk[k] = tj[k*salto] # Malla para cada eje X,Y Xi, Yi = np.meshgrid(xi,tk) U = np.transpose(U) fig_3D = plt.figure() graf_3D = fig_3D.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') graf_3D.plot_wireframe(Xi,Yi,U, color ='blue') graf_3D.plot(xi[0],tk[1],U[1,0],'o',color ='orange') graf_3D.plot(xi[1],tk[1],U[1,1],'o',color ='green') graf_3D.plot(xi[2],tk[1],U[1,2],'o',color ='green') graf_3D.plot(xi[1],tk[2],U[2,1],'o',color ='salmon', label='U[i,j+1]') graf_3D.set_title('EDP Parabólica') graf_3D.set_xlabel('x') graf_3D.set_ylabel('t') graf_3D.set_zlabel('U') graf_3D.legend() graf_3D.view_init(35, -45) plt.show()
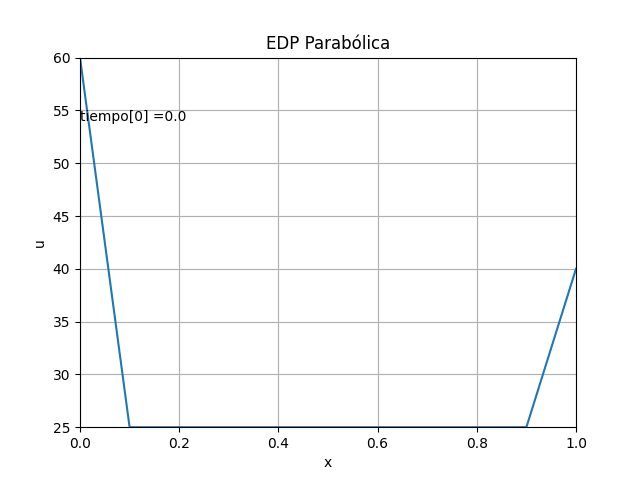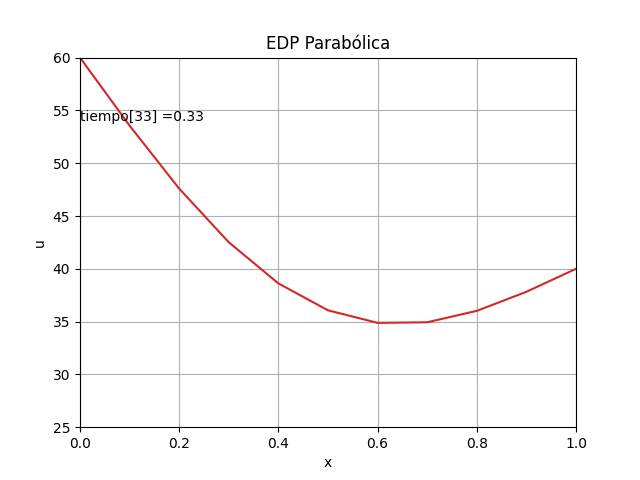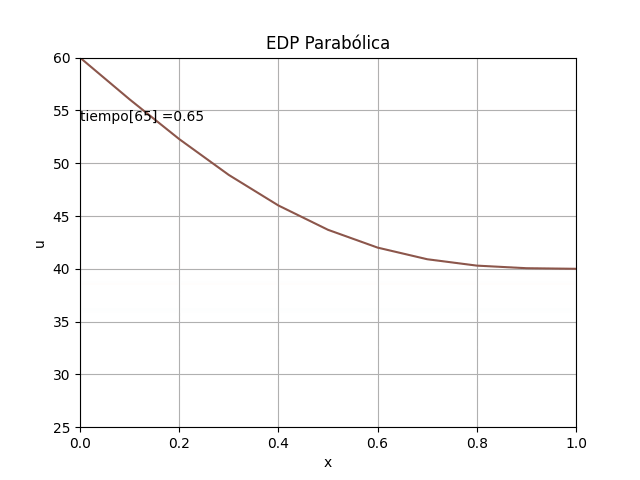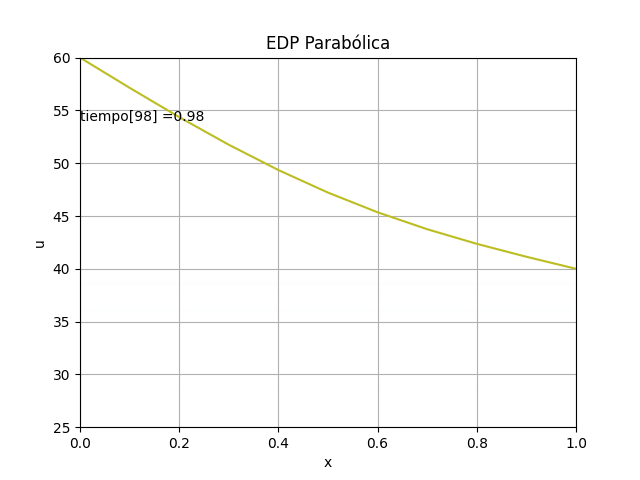
1.3 Gráficas EDP Parabólica, método explícito en 2D con animación
La animación en 2D para la EDP parabólica método explícito se añade, luego de comentar el #plt.show() anterior
# GRAFICA CON ANIMACION 2D-------- # import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.animation as animation unmetodo = 'EDP Parabólica - Método explícito' narchivo = 'EdpParabolica' # nombre archivo GIF # Parametros de trama/foto retardo = 500 # milisegundos entre tramas # GRAFICA animada en fig_ani fig_ani, graf_ani = plt.subplots() # Lineas y puntos base linea_f, = graf_ani.plot(xi,u[:,0]) graf_ani.axhline(0, color='k') # Eje en x=0 maximoy = np.max(u) txt_y = maximoy*(1-0.1) txt_f = graf_ani.text(xi[0],txt_y,'tiempo:', horizontalalignment='left') # Configura gráfica graf_ani.set_xlim([xi[0],xi[ultimox]]) graf_ani.set_ylim([ np.min(u),maximoy]) graf_ani.set_title(unmetodo) graf_ani.set_xlabel('x') graf_ani.set_ylabel('u') #graf_ani.legend() graf_ani.grid() # Nueva Trama def unatrama(i,xi,u): # actualiza cada linea linea_f.set_ydata(u[:,i]) linea_f.set_xdata(xi) linea_f.set_label('tiempo linea: '+str(i)) if (i<=9): # color de la línea lineacolor = 'C'+str(i) else: numcolor = i%10 lineacolor = 'C'+str(numcolor) linea_f.set_color(lineacolor) txt_f.set_text('tiempo['+str(i)+'] = ' + str(i*dt)) return linea_f, txt_f, # Limpia Trama anterior def limpiatrama(): linea_f.set_ydata(np.ma.array(xi, mask=True)) linea_f.set_label('') txt_f.set_text('') return linea_f, txt_f, # contador de tramas i = np.arange(0,len(tk),1) ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig_ani, unatrama, i , fargs=(xi,u), init_func=limpiatrama, interval=retardo, blit=True) # Graba Archivo GIFAnimado y video ani.save(narchivo+'_animado.gif', writer='imagemagick') #ani.save(narchivo+'.mp4') plt.draw() plt.show()
1.4 Gráficas EDP Parabólica, método explícito en 3D con animación
Para el caso de animación 3D, se cambia la sección de animación del algoritmo anterior por:
# GRAFICA CON ANIMACION 3D-------- # import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.animation as animation unmetodo = 'EDP Parabólica - Método explícito' narchivo = 'EdpParabolica2' # nombre archivo GIF # Parametros de trama/foto retardo = 500 # milisegundos entre tramas # GRAFICA animada en fig_ani fig_ani3D = plt.figure() graf_ani3 = fig_ani3D.add_subplot(projection='3d') # Lineas y puntos base ##graf_ani3.plot_wireframe(Xi,Yi,U, ## color ='blue',label='EDP Parabólica') punto_a, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],tk[0],U[1,0],'o',color ='green') punto_b, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],tk[0],U[1,0],'o', color ='salmon',label='U[i,j+1]') linea_c, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],tk[0],U[1,0],'-',color ='blue') # Configura gráfica graf_ani3.set_xlim(min(xi),max(xi)) graf_ani3.set_ylim(min(tk),max(tk)) graf_ani3.set_title(unmetodo) graf_ani3.set_xlabel('x') graf_ani3.set_ylabel('t') graf_ani3.set_zlabel('U') graf_ani3.legend() graf_ani3.grid() graf_ani3.view_init(35, -45) mallaEDP = None # Nueva Trama def unatrama(i,xi,tk,U,k): f = i//k c = i%k # actualiza cada punto punto_a.set_data([[xi[c],xi[c+1],xi[c+2]], [tk[f],tk[f],tk[f]]]) punto_a.set_3d_properties([U[f,c],U[f,c+1],U[f,c+2]]) punto_b.set_data([xi[c+1]],[tk[f+1]]) punto_b.set_3d_properties([U[f+1,c+1]]) linea_c.set_data(xi[0:c+2],[tk[f+1]]*(c+2)) linea_c.set_3d_properties([U[f+1,0:c+2]]) global mallaEDP if mallaEDP: graf_ani3.collections.remove(mallaEDP) mallaEDP = graf_ani3.plot_wireframe(Xi[0:f+1,:], Yi[0:f+1,:], U[0:f+1,:], color ='blue', label='EDP Parabólica') return (punto_a,punto_b,linea_c) # contador de tramas k = len(xi)-2 k2 = k*(len(tk)-1) i = np.arange(0,k2,1) ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig_ani3D, unatrama, i , fargs=(xi,tk,U,k), interval=retardo, blit=False) # Graba Archivo GIFAnimado y video ani.save(narchivo+'_animado.gif', writer='imagemagick') #ani.save(narchivo+'.mp4') #plt.draw() plt.show()
EDP Parabólica [ concepto ] [ ejercicio ]
2. EDP Parabólicas método implícito
Puesto que la solución de la tabla de resultados en U es la misma que el los dos métodos explícito e implícito, solo se adjunta la parte de la animación.
Para el caso del la gráfica 3D del método implícito se cambia la sección de gráfica animada por:
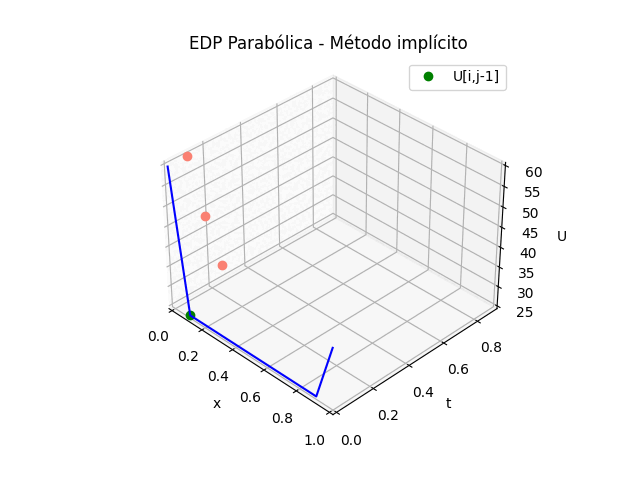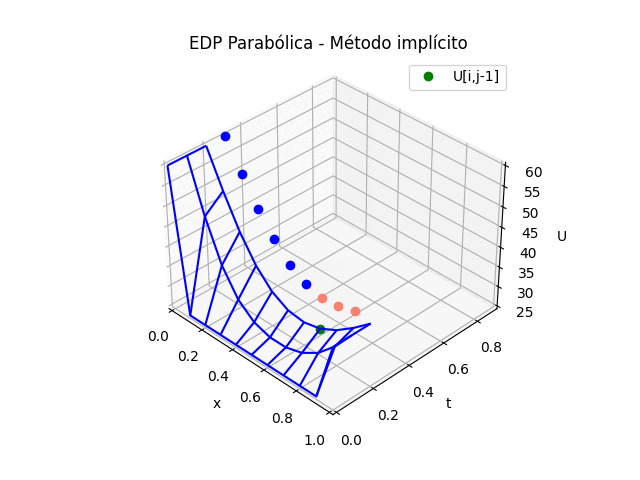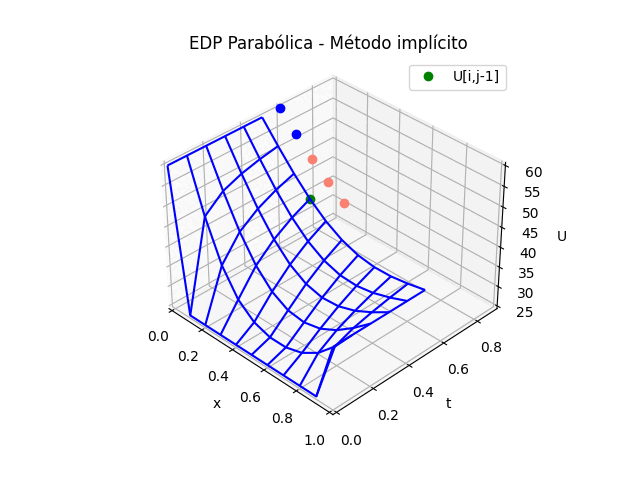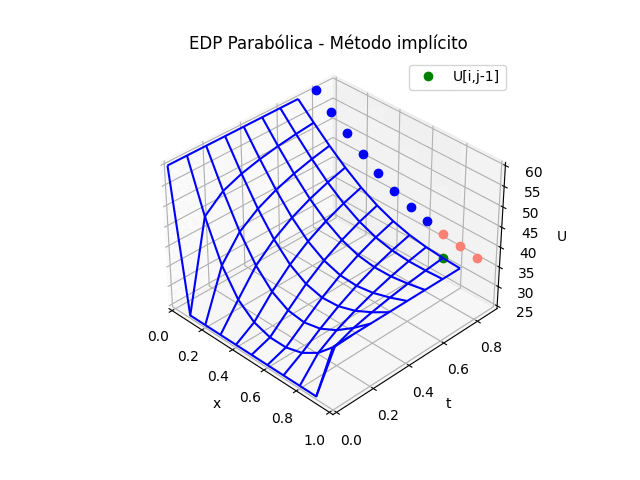
# GRAFICA CON ANIMACION 3D-------- # import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.animation as animation unmetodo = 'EDP Parabólica - Método implícito' narchivo = 'EdpParabImpli' # nombre archivo GIF # Parametros de trama/foto retardo = 500 # milisegundos entre tramas # GRAFICA animada en fig_ani fig_ani3D = plt.figure() graf_ani3 = fig_ani3D.add_subplot(projection='3d') # Lineas y puntos base ##graf_ani3.plot_wireframe(Xi,Yi,U, ## color ='blue',label='EDP Parabólica') punto_a, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],tk[0],U[1,0],'o',color ='salmon') punto_b, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],tk[0],U[1,0],'o', color ='green',label='U[i,j-1]') linea_c, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],tk[0],U[1,0],'o',color ='blue') # Configura gráfica graf_ani3.set_xlim(min(xi),max(xi)) graf_ani3.set_ylim(min(tk),max(tk)) graf_ani3.set_title(unmetodo) graf_ani3.set_xlabel('x') graf_ani3.set_ylabel('t') graf_ani3.set_zlabel('U') graf_ani3.legend() graf_ani3.grid() graf_ani3.view_init(35, -45) mallaEDP = None # Nueva Trama def unatrama(i,xi,tk,U,k): f = i//k c = i%k # actualiza cada punto punto_a.set_data([[xi[c],xi[c+1],xi[c+2]], [tk[f+1],tk[f+1],tk[f+1]]]) punto_a.set_3d_properties([U[f+1,c],U[f+1,c+1],U[f+1,c+2]]) punto_b.set_data([xi[c+1]],[tk[f]]) punto_b.set_3d_properties([U[f,c+1]]) linea_c.set_data(xi[0:c],[tk[f+1]]*(c)) linea_c.set_3d_properties([U[f+1,0:c]]) global mallaEDP if mallaEDP: graf_ani3.collections.remove(mallaEDP) mallaEDP = graf_ani3.plot_wireframe(Xi[0:f+1,:], Yi[0:f+1,:], U[0:f+1,:], color ='blue', label='EDP Parabólica') return (punto_a,punto_b,linea_c) # contador de tramas k = len(xi)-2 k2 = k*(len(tk)-1) i = np.arange(0,k2,1) ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig_ani3D, unatrama, i , fargs=(xi,tk,U,k), interval=retardo, blit=False) # Graba Archivo GIFAnimado y video ani.save(narchivo+'_animado.gif', writer='imagemagick') #ani.save(narchivo+'.mp4') #plt.draw() plt.show()
EDP Parabólica [ concepto ] [ ejercicio ]
2. EDP Elípticas método iterativo
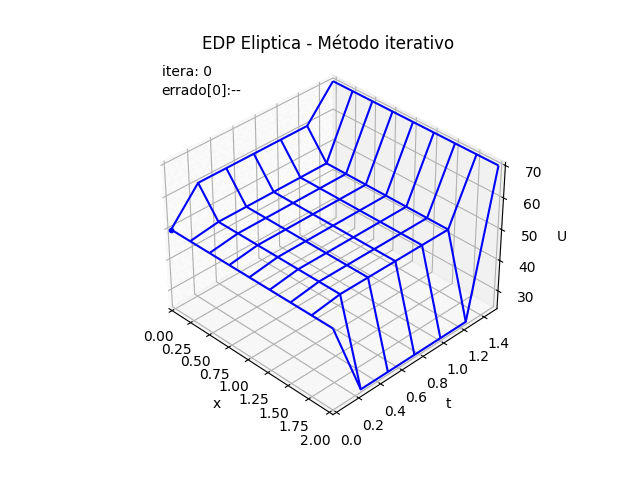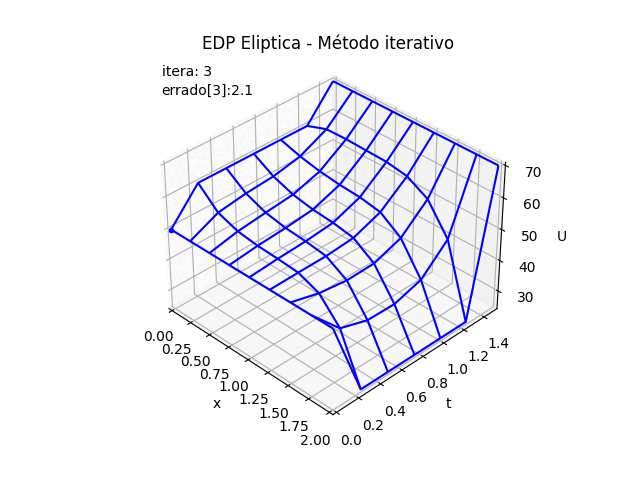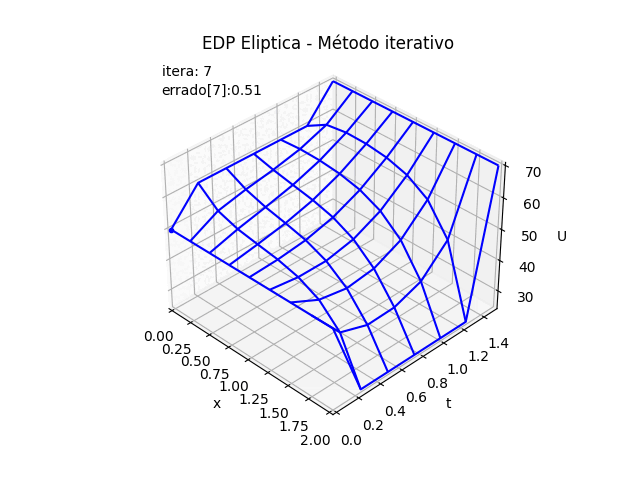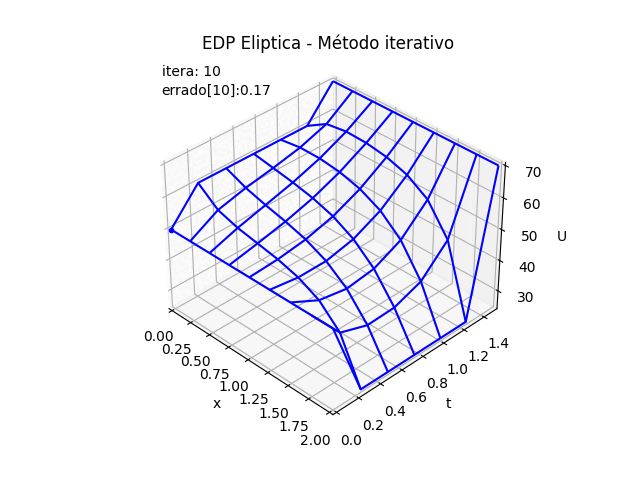
Al algoritmo desarrollado en EDP Elípticas método iterativo, se crean una lista para almacenar los valores de la matriz U por cada iteración, se usan para graficar cada iteración.
# Ecuaciones Diferenciales Parciales # Elipticas. Método iterativo import numpy as np # INGRESO # Condiciones iniciales en los bordes Ta = 60 # izquierda Tb = 25 # derecha #Tc = 50 # inferior fxc = lambda x: 50+0*x # función inicial inferior # Td = 70 # superior fxd = lambda x: 70+0*x # función inicial superior # dimensiones de la placa x0 = 0 # longitud en x xn = 2 y0 = 0 # longitud en y yn = 1.5 # discretiza, supone dx=dy dx = 0.25 # Tamaño de paso dy = dx iteramax = 100 tolera = 0.0001 verdigitos = 2 # decimales a mostrar en tabla de resultados # PROCEDIMIENTO xi = np.arange(x0,xn+dx,dx) yj = np.arange(y0,yn+dy,dy) n = len(xi) m = len(yj) # Matriz u u = np.zeros(shape=(n,m),dtype = float) # llena u con valores en fronteras u[0,:] = Ta # izquierda u[n-1,:] = Tb # derecha fic = fxc(xi) u[:,0] = fic # Tc inferior fid = fxd(xi) u[:,m-1] = fid # Td superior # valor inicial de iteración dentro de u # promedio = (Ta+Tb+Tc+Td)/4 promedio = (Ta+Tb+np.max(fic)+np.max(fid))/4 u[1:n-1,1:m-1] = promedio np.set_printoptions(precision=verdigitos) print('u inicial:') print(np.transpose(u)) # iterar puntos interiores U_3D = [np.copy(u)] U_error = ['--'] itera = 0 converge = False while (itera<=iteramax and converge==False): itera = itera +1 Uantes = np.copy(u) for i in range(1,n-1): for j in range(1,m-1): u[i,j] = (u[i-1,j]+u[i+1,j]+u[i,j-1]+u[i,j+1])/4 diferencia = u - Uantes errado_u = np.max(np.abs(diferencia)) if (errado_u<tolera): converge=True U_3D.append(np.copy(u)) U_error.append(np.around(errado_u,verdigitos)) if itera<=3: np.set_printoptions(precision=verdigitos) print('itera:',itera-1,' ; ','u:') print(np.transpose(u)) print('errado_u: ', errado_u) if itera==4: print('... continua') # SALIDA print('Método Iterativo EDP Elíptica') print('iteraciones:',itera,' converge = ', converge) print('xi:', xi) print('yj:', yj) print('Tabla de resultados en malla EDP Elíptica') print('j, U[i,j]') for j in range(m-1,-1,-1): print(j,u[:,j]) # GRAFICA en 3D ------ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Malla para cada eje X,Y Xi, Yi = np.meshgrid(xi, yj) U = np.transpose(u) # ajuste de índices fila es x fig_3D = plt.figure() graf_3D = fig_3D.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') graf_3D.plot_wireframe(Xi,Yi,U, color ='blue') graf_3D.plot(Xi[1,0],Yi[1,0],U[1,0],'o',color ='orange') graf_3D.plot(Xi[1,1],Yi[1,1],U[1,1],'o',color ='red', label='U[i,j]') graf_3D.plot(Xi[1,2],Yi[1,2],U[1,2],'o',color ='salmon') graf_3D.plot(Xi[0,1],Yi[0,1],U[0,1],'o',color ='green') graf_3D.plot(Xi[2,1],Yi[2,1],U[2,1],'o',color ='salmon') graf_3D.set_title('EDP elíptica') graf_3D.set_xlabel('x') graf_3D.set_ylabel('y') graf_3D.set_zlabel('U') graf_3D.legend() graf_3D.view_init(35, -45) plt.show() # GRAFICA CON ANIMACION 3D-------- # import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.animation as animation unmetodo = 'EDP Eliptica - Método iterativo' narchivo = 'EdpElipticaItera' # nombre archivo GIF # Parametros de trama/foto retardo = 500 # milisegundos entre tramas # GRAFICA animada en fig_ani fig_ani3D = plt.figure() graf_ani3 = fig_ani3D.add_subplot(projection='3d') # Lineas y puntos base punto_a, = graf_ani3.plot(xi[0],yj[0],U[0,0],'.',color ='blue') # Configura gráfica graf_ani3.set_xlim(min(xi),max(xi)) graf_ani3.set_ylim(min(yj),max(yj)) graf_ani3.set_title(unmetodo) graf_ani3.set_xlabel('x') graf_ani3.set_ylabel('t') graf_ani3.set_zlabel('U') # graf_ani3.legend() graf_ani3.grid() graf_ani3.view_init(35, -45) etiqueta_i ='itera: '+str(0) etiqueta_err = 'errado['+str(0)+']: '+str(U_error[0]) txt_i = graf_ani3.text2D(0.05, 0.95, etiqueta_i, transform=graf_ani3.transAxes) txt_errado = graf_ani3.text2D(0.05, 0.90, etiqueta_err, transform=graf_ani3.transAxes) mallaEDP = None # Nueva Trama def unatrama(i,xi,yj,U_3D,U_error): etiqueta_i ='itera: '+str(i) txt_i.set_text(etiqueta_i) etiqueta_err = 'errado['+str(i)+']: '+str(U_error[i]) txt_errado.set_text(etiqueta_err) global mallaEDP if mallaEDP: graf_ani3.collections.remove(mallaEDP) mallaEDP = graf_ani3.plot_wireframe(Xi,Yi, np.transpose(U_3D[i]), color ='blue') return (txt_i,txt_errado,) # contador de tramas k = 11 #len(U_3D) i = np.arange(0,k,1) ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig_ani3D, unatrama, i , fargs=(xi,yj,U_3D,U_error), interval=retardo, blit=False) # Graba Archivo GIFAnimado y video ani.save(narchivo+'_animado.gif', writer='imagemagick') #ani.save(narchivo+'.mp4') #plt.draw() plt.show()