Ejercicio: 2Eva_IT2012_T3_MN EDO Taylor 2 Contaminación de estanque
La ecuación a resolver con Taylor es:
s'- \frac{26s}{200-t} - \frac{5}{2} = 0Para lo que se plantea usar la primera derivada:
s'= \frac{26s}{200-t}+\frac{5}{2}con valores iniciales de s(0) = 0, h=0.1
La fórmula de Taylor para tres términos es:
s_{i+1}= s_{i}+s'_{i}h + \frac{s''_{i}}{2}h^2 + errorPara el desarrollo se compara la solución con dos términos, tres términos y Runge Kutta.
1. Solución con dos términos de Taylor
Iteraciones
i = 0, t0 = 0, s(0)=0
s'_{0}= \frac{26s_{0}}{200-t_{0}}+\frac{5}{2} = \frac{26(0)}{200-0}+\frac{5}{2} = \frac{5}{2} s_{1}= s_{0}+s'_{0}h = 0+ \frac{5}{2}*0.1= 0.25t1 = t0+h = 0+0.1 = 0.1
i=1
s'_{1}= \frac{26s_{1}}{200-t_{1}}+\frac{5}{2} = \frac{26(0.25)}{200-0.1}+\frac{5}{2} = 2.5325 s_{2}= s_{1}+s'_{1}h = 0.25 + (2.5325)*0.1 = 0.5032
t2 = t1+h = 0.1+0.1 = 0.2
i=2,
resolver como tarea
2. Resolviendo con Python
estimado [xi,yi Taylor,yi Runge-Kutta, diferencias] [[ 0.0 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00] [ 0.1 2.5000e-01 2.5163e-01 -1.6258e-03] [ 0.2 5.0325e-01 5.0655e-01 -3.2957e-03] [ 0.3 7.5980e-01 7.6481e-01 -5.0106e-03] [ 0.4 1.0197e+00 1.0265e+00 -6.7714e-03] [ 0.5 1.2830e+00 1.2916e+00 -8.5792e-03] [ 0.6 1.5497e+00 1.5601e+00 -1.0435e-02] [ 0.7 1.8199e+00 1.8322e+00 -1.2339e-02] [ 0.8 2.0936e+00 2.1079e+00 -1.4294e-02] [ 0.9 2.3710e+00 2.3873e+00 -1.6299e-02] [ 1.0 2.6519e+00 2.6703e+00 -1.8357e-02] [ 1.1 2.9366e+00 2.9570e+00 -2.0467e-02] [ 1.2 3.2250e+00 3.2476e+00 -2.2632e-02] [ 1.3 3.5171e+00 3.5420e+00 -2.4853e-02] [ 1.4 3.8132e+00 3.8403e+00 -2.7129e-02] [ 1.5 4.1131e+00 4.1426e+00 -2.9464e-02] [ 1.6 4.4170e+00 4.4488e+00 -3.1857e-02] [ 1.7 4.7248e+00 4.7592e+00 -3.4310e-02] [ 1.8 5.0368e+00 5.0736e+00 -3.6825e-02] [ 1.9 5.3529e+00 5.3923e+00 -3.9402e-02] [ 2.0 5.6731e+00 5.7152e+00 -4.2043e-02]] error en rango: 0.04204310894163932
2. Algoritmo en Python
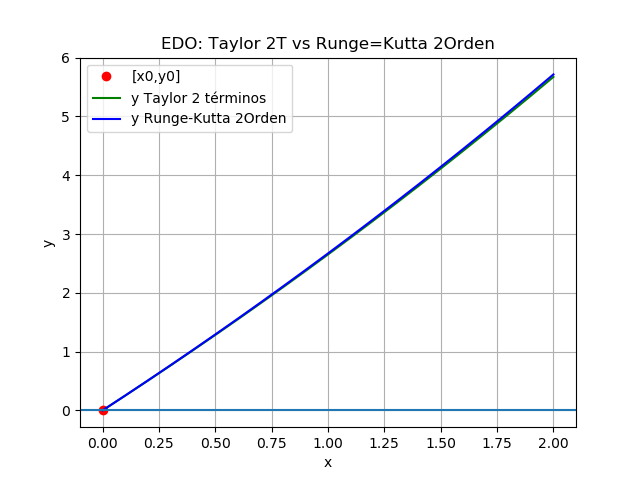
# EDO. Método de Taylor 3 términos # estima la solucion para muestras espaciadas h en eje x # valores iniciales x0,y0 # entrega arreglo [[x,y]] import numpy as np def edo_taylor2t(d1y,x0,y0,h,muestras): tamano = muestras + 1 estimado = np.zeros(shape=(tamano,2),dtype=float) # incluye el punto [x0,y0] estimado[0] = [x0,y0] x = x0 y = y0 for i in range(1,tamano,1): y = y + h*d1y(x,y) # + ((h**2)/2)*d2y(x,y) x = x+h estimado[i] = [x,y] return(estimado) def rungekutta2(d1y,x0,y0,h,muestras): tamano = muestras + 1 estimado = np.zeros(shape=(tamano,2),dtype=float) # incluye el punto [x0,y0] estimado[0] = [x0,y0] xi = x0 yi = y0 for i in range(1,tamano,1): K1 = h * d1y(xi,yi) K2 = h * d1y(xi+h, yi + K1) yi = yi + (K1+K2)/2 xi = xi + h estimado[i] = [xi,yi] return(estimado) # PROGRAMA PRUEBA # 2Eva_IIT2016_T3_MN EDO Taylor 2, Tanque de agua # INGRESO. # d1y = y' = f, d2y = y'' = f' d1y = lambda x,y: 26*y/(200-x)+5/2 x0 = 0 y0 = 0 h = 0.1 muestras = 20 # PROCEDIMIENTO puntos = edo_taylor2t(d1y,x0,y0,h,muestras) xi = puntos[:,0] yi = puntos[:,1] # Con Runge Kutta puntosRK2 = rungekutta2(d1y,x0,y0,h,muestras) xiRK2 = puntosRK2[:,0] yiRK2 = puntosRK2[:,1] # diferencias diferencias = yi-yiRK2 error = np.max(np.abs(diferencias)) tabla = np.copy(puntos) tabla = np.concatenate((puntos,np.transpose([yiRK2]), np.transpose([diferencias])), axis = 1) # SALIDA np.set_printoptions(precision=4) print('estimado[xi,yi Taylor,yi Runge-Kutta, diferencias]') print(tabla) print('error en rango: ', error) # Gráfica import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot(xi[0],yi[0],'o', color='r', label ='[x0,y0]') plt.plot(xi[0:],yi[0:],'-', color='g', label ='y Taylor 2 términos') plt.plot(xiRK2[0:],yiRK2[0:],'-', color='blue', label ='y Runge-Kutta 2Orden') plt.axhline(y0/2) plt.title('EDO: Taylor 2T vs Runge=Kutta 2Orden') plt.xlabel('x') plt.ylabel('y') plt.legend() plt.grid() plt.show()
Usando Taylor con 3 términos
estimado [xi, yi, d1yi, d2yi ] [[0. 0. 2.5 0.325 ] [0.1 0.251625 2.53272761 0.32958302] [0.2 0.50654568 2.56591685 0.33423301] [0.3 0.76480853 2.59957447 0.33895098] [0.4 1.02646073 2.63370731 0.34373796] [0.5 1.29155015 2.66832233 0.348595 ] [0.6 1.56012536 2.70342658 0.35352316] [0.7 1.83223563 2.73902723 0.35852351] [0.8 2.10793097 2.77513155 0.36359715] [0.9 2.38726211 2.81174694 0.36874519] [1. 2.67028053 2.84888087 0.37396876] [1.1 2.95703846 2.88654098 0.37926901] [1.2 3.24758891 2.92473497 0.3846471 ] [1.3 3.54198564 2.96347069 0.39010422] [1.4 3.84028323 3.00275611 0.39564157] [1.5 4.14253705 3.04259931 0.40126036] [1.6 4.44880328 3.08300849 0.40696184] [1.7 4.75913894 3.12399199 0.41274727] [1.8 5.07360187 3.16555827 0.41861793] [1.9 5.39225079 3.2077159 0.42457511] [2. 5.71514526 0. 0. ]]